reading-notes
This Repo required for Asac labs class 2
Project maintained by ManarAbdelkarim Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
# Data Science Primer
There are 5 core steps:
1- Exploratory Analysis
First, “get to know” the data. This step should be quick, efficient, and decisive.
2- Data Cleaning
Then, clean your data to avoid many common pitfalls. Better data beats fancier algorithms.
a- Remove Unwanted observations
b- Fix Structural Errors
c- Filter Unwanted Outliers
d- Handle Missing Data
1- Dropping observations that have missing values
2- Imputing the missing values based on other observations
how to deal with missing data?
a- Missing categorical data:
- Missing categorical data
The best way to handle missing data for
this categorical features is to simply label them as ’Missing’!
b- Missing numeric data
- For missing numeric data, you should flag and fill the values.
3- Feature Engineering
Next, help your algorithms “focus” on what’s important by creating new features.
a- Infuse Domain Knowledge
b- Create Interaction Features
c- Combine Sparse Classes
d- Add Dummy Variables
e- Remove Unused Features
4- Algorithm Selection
Choose the best, most appropriate algorithms without wasting your time.
- There are 3 common types of regularized linear regression algorithms:
a- Lasso Regression
Lasso, or LASSO, stands for Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator.
* Lasso regression penalizes the absolute size of coefficients
b- Ridge Regression
* Ridge regression penalizes the squared size of coefficients.
c- Elastic-Net
Elastic-Net is a compromise between Lasso and Ridge.
- base models of decision trees:
a- Random forests
b- Boosted trees
5- Model Training
a- Split Dataset
b- Fit and Tune Models
c- Select Winning Model
Finally, train your models. This step is pretty formulaic once you’ve done the first

## Key Terminology :
- ’
Model’ - a set of patterns learned from data. Algorithm- a specific ML process used to train a model.Training data- the dataset from which the algorithm learns the model.Test data- a new dataset for reliably evaluating model performance.Features- Variables (columns) in the dataset used to train the model.Target variable- A specific variable you’re trying to predict.Observations- Data points (rows) in the dataset.Sparse classes(in categorical features) are those that have very few total observations. They can be problematic for certain machine learning algorithms, causing models to be overfit.Unused featuresare those that don’t make sense to pass into our machine learning algorithms.Redundant featureswould typically be those that have been replaced by other features that you’ve added during feature engineering.
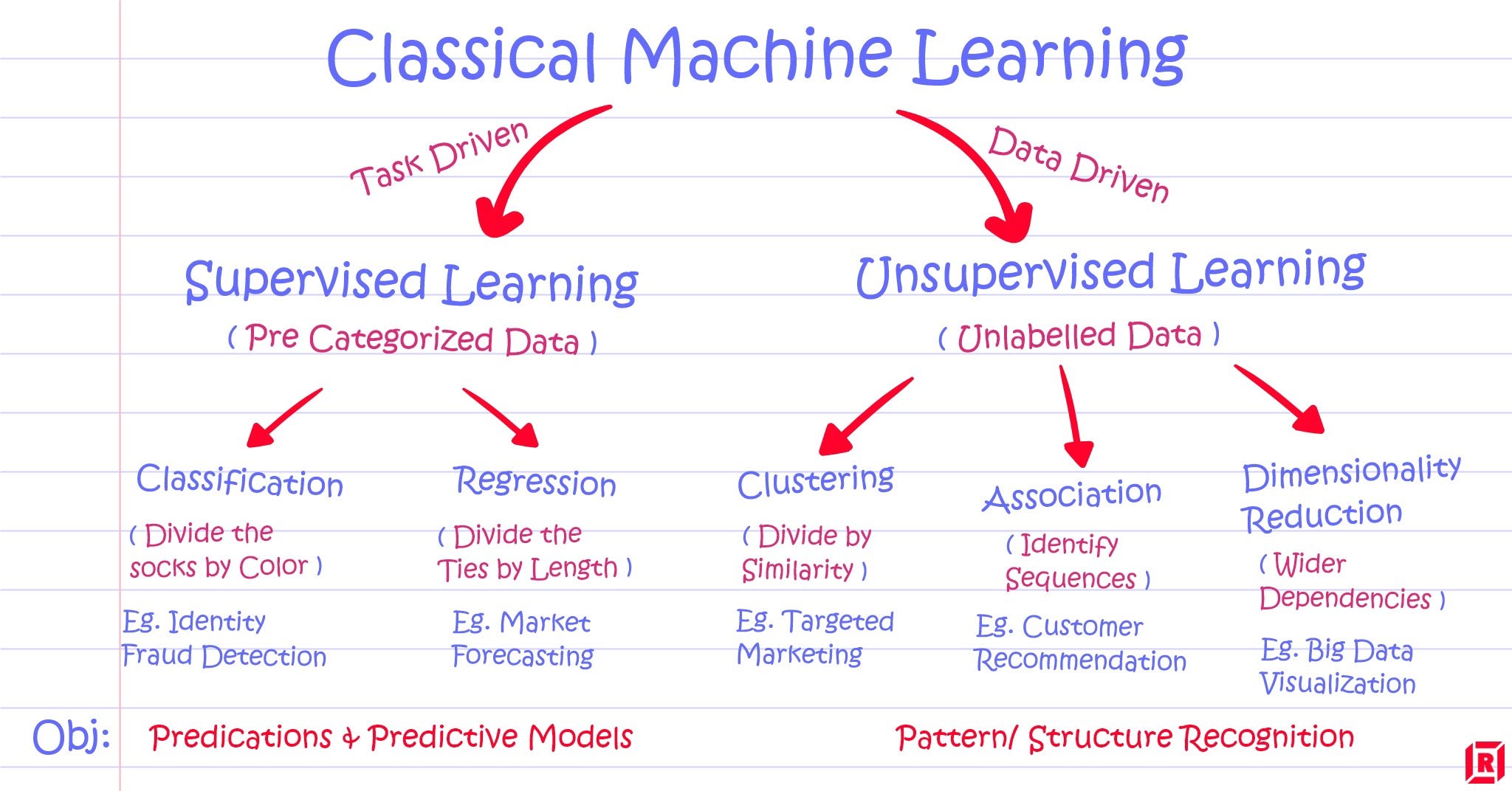
Machine Learning Tasks:
A task is a specific objective for your algorithms.