reading-notes
This Repo required for Asac labs class 2
Project maintained by ManarAbdelkarim Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Cryptography
Cryptography, or the art and science of encrypting sensitive information, was once exclusive to the realms of government, academia, and the military. However, with recent technological advancements, cryptography has begun to permeate all facets of everyday life.

Caesar Cipher
In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as shift cipher, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. The Caesar cipher is named after Julius Caesar, who used it, more than 2000 years ago, to protect messages of military significance.

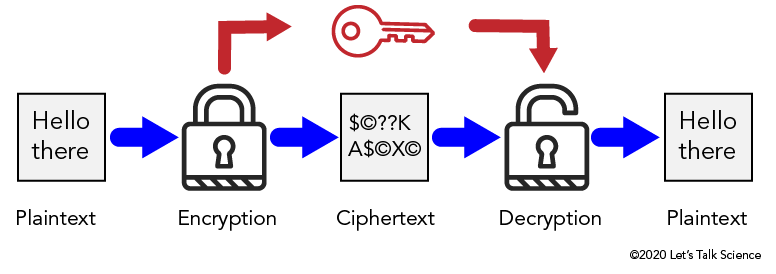
Encryption:
Encryption is the method by which information is converted into secret code that hides the information’s true meaning. The science of encrypting and decrypting information is called cryptography.(scrambling the data according to a secret key )
decryption:
Decryption is taking encoded or encrypted text or other data and converting it back into text you or the computer can read and understand. This term could be used to describe a method of unencrypting the data manually or unencrypting the data using the proper codes or keys.( recovering the original data from scrambled data by using the secret key.)
cracking:
Cracking is a technique used to breach computer software or an entire computer security system, and with malicious intent. Though functionally the same as hacking, cracking is strictly used in a criminal sense. Learn how cracking works, how to recognize it, and how you can protect yourself against getting cracked.(uncovering the original data without knowing the secret, by using a variety of clever techniques.)

three main techniques for cracking:
- Frequency analysis
- Analyze the letter frequency of the ciphertext, and try to deduce the shift value.
- known plaintext
- In order to crack you need enough information to verify if the key you’re trying is correct.
- and brute force.
- we try every possibility, until we find a reasonable looking plaintext.