reading-notes
This Repo required for Asac labs class 2
Project maintained by ManarAbdelkarim Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
JavaScript
Chapter 2: “Basic JavaScript Instructions”
STATEMENTS:
What is a script ?
A script is a series of instructions that a computer can follow one-by-one.
What is a Statement ?
statement is each individual instruction or step of the script, Statements should end with a semicolon.
what are code blocks?
the curly braces that Some statements are surrounded by. The closing curlybrace is not followed by a semicolon.
What is a VARIABLE?
A script will have to temporarily store the bits of information it needs to do its job. It can store this data in variables. in a variable can change (or vary) each time a script runs. structure:
variable-key variable-name;
assign a value to the variable:r
variable-name = variable-value;

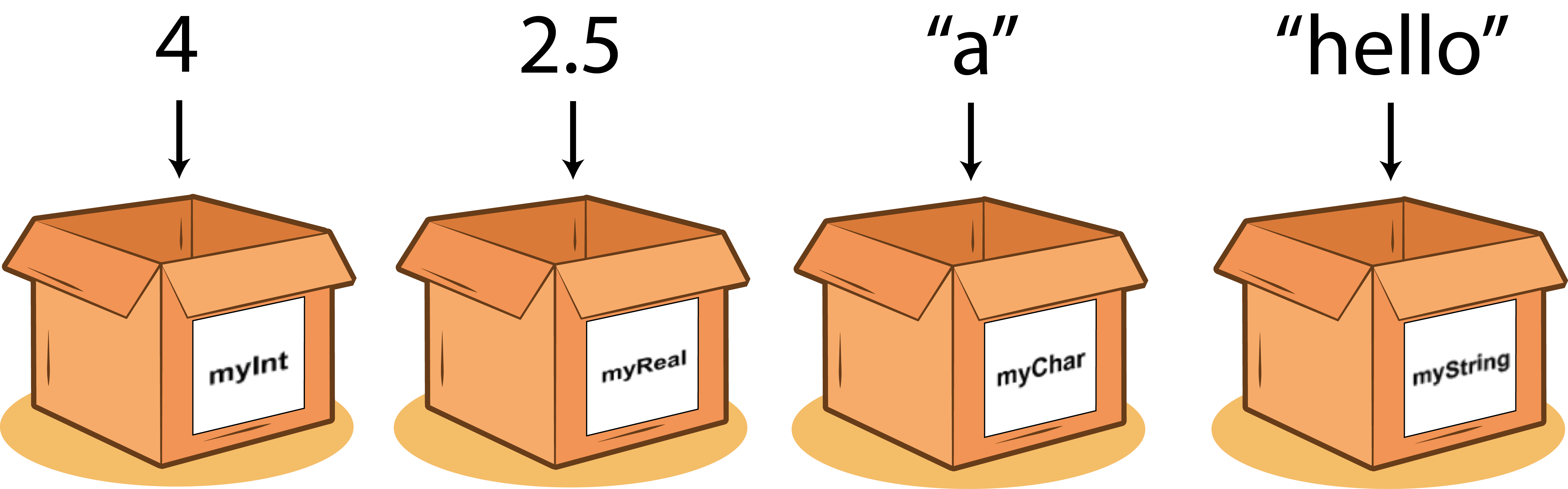
DATA TYPES:
-
NUMERIC DATA TYPE
- The numeric data type handles, an integer or a floating-point number. numbers.
- STRING DATA TYPE
- The strings data type consists of letters and other characters.
- BOOLEAN DATA TYPE
- Boolean data types can have one of two values: true or false.
CHANGING THE VALUE OF A VARIABLE :
variable-name = variable-value;
RULES FOR NAMING VARIABLES
-
The name must begin with a letter,($),or(_).It must not start with a number.
-
you must not use (-) or (.) in a variable name.
-
All variables are case sensitive.
-
Use a name that describes the kind of information that the variable stores.
-
You cannot use keywords or reserved words.
-
If your variable name is made up of more than one word, use a capital letter for the first letter of every word after the first word.
ARRAYS
what is an array ?
An array is a special type of variable. It doesn’t just store one value; it stores a list of values. you can use it on a list or a set of values that are related to each other.
How to create an (literal)Array?
var Array-Name = [value1,value2…valueN]
How to create an Array with n array constructor?
var Array-Name = new Array(value1 , value2,valueN);
Note
The array literal is preferred over the array constructor when creating arrays.
VALUES IN ARRAYS
Values in an array are accessed as if they are in a numbered list. It is important to know that the numbering of this list starts at zero (not one).
ACCESSING & CHANGING VALUES IN AN ARRAY
Update the an item in the array: colors[the-item’s-index-number] = NewValue ;
EXPRESSIONS
what is an expression?
An expression evaluates into (results in) a single value.
types of expressions:
- EXPRESSIONS THAT JUST ASSIGN A
VALUE TO A VARIABLE
var variable-name = variable-value;
- EXPRESSIONS THAT USE TWO OR
MORE VALUES TO RETURN A
SINGLE VALUE
var variable-name = value1 (* - + % / ) value2
OPERATORS
Expressions rely on things called operators; they allow programmers to create a single value from one or more values.
Operators’ Types:
-
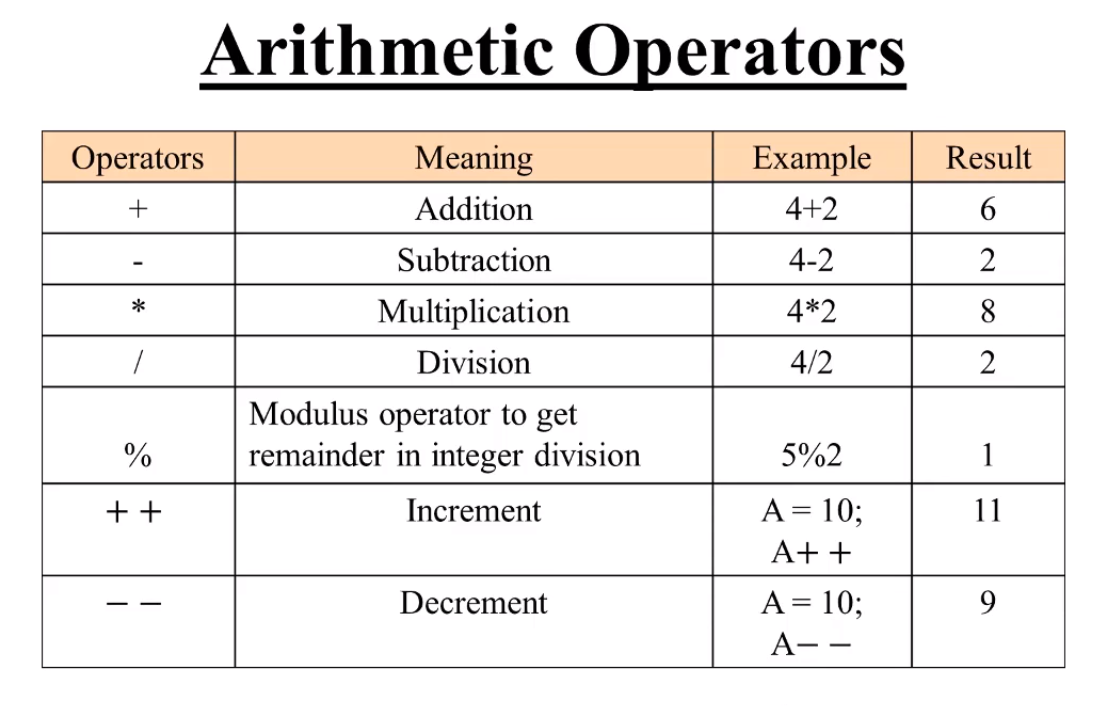
ARITHMETIC OPERATORS
- JavaScript contains the following mathematical operators, which you can use with numbers. You may remember some from math class.
\
- STRING OPERATOR
- There is just one string operator: the+ symbol. It is used to join the strings on either side of it.
-
two operators are used in string operators:
- = (normal operator sign a value)
- += (concatenation operator combine old and new values)
Sammary:
- A script is made up of a series of statements. Each statement is like a step in a recipe.
- Scripts contain very precise instructions. For example, you might specify that a value must be remembered before creating a calculation using that value.
- Variables are used to temporarily store pieces of information used in the script.
- Arrays are special types of variables that store more than one piece of related information.
- JavaScript distinguishes between numbers (0-9), strings (text), and Boolean values (true or false).
- Expressions evaluate into a single value.
- Expressions rely on operators to calculate a value.
Chapter 4: “DECISIONS & LOOPS”
Using a flowchart will help making decisions
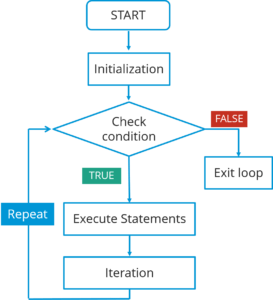
Evaluating a Condition and Conditional Statment
components of decision:
-
EVALUATION OF A CONDITION: An expression is evaluated, which returns a value
-
CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS: A conditional statement says what to do in a given situation
### USING COMPARISON OPERATORS:
var var1 = value1;
var var2 = vakue2;
var Comparison-variable = var1 (>,<,>=,<=,==,===,!=,!==) var2;
Logical Operatrs:
Logical operators are used to determine the logic between variables or values.
- && -> Logical and
-
-> Logical or - ! -> Logical not
If Statement:
The if statement evaluates (or checks) a condition. If the condition evaluates to true, any statements in the subsequent code block are executed.
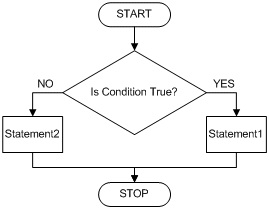
IF…ELSE STATEMENTS
The if…else statement checks a condition. If it resolves to true the first code block is executed. If the condiion resolves to false the second code block is run instead.
| ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
HTML
Chapter 2: “Text”
Headings:
<h1> <h2> <h3> <h4> <h5> <h6>
-
H1 is the biggest and h6 is the smallest.
-
the diffrence between headings is the level of important
- i.e. h1 for the main headings and subheadings for the subheadings
Paragraphs: <p>
- To create a paragraph
<p>the paragraph you want</p>
Bold & Italic
bold:<b>
<b>This is bold text</b>
The Result: This is bold text
Italic:<i>
<i>This is Italic text</i>
The Result: This is Italic text
Superscript: <sup>
value<sup>th</sup>
The Result: valueth
Subscript: <sub>
value<sub>th</sub>
The Result: valueth
White Space:
white space collapsing: When the browser comes across two or more spaces next to each other, it only displays one space.
<p>Some text</p>
The Result: <p>Some text</p>
Line Breaks:<br>
Some<br>text
The Result:
Some
text
Horizontal Rules: <hr>
some <hr>text
The Result:
some <hr>text
Semantic Markup:
Semantic Markup: elements that are not intended to affect the structure of your web pages, but they do add extra information to the pages — they are known as semantic markup. i.e. <em><blockquote>
Strong:<strong>
<strong>strong text</strong>
The Result: strong text
Emphasis:<em>
The <em> element indicates emphasis that subtly changes the meaning of a sentence. By default browsers will show the contents of an <em> element in italic.
text <em>Emphasis</em> text
The Result: text Emphasis text
Quotations:<blockquote><q>
<blockquote>:
The <blockquote> element is used for longer quotes that take up an entire paragraph. Browsers tend to indent the contents of the <blockquote>
<blockquote> element is used for longer quotes that take up an entire paragraph. Browsers tend to indent the contents of the </blockquote>
The Result:
element is used for longer quotes that take up an entire paragraph. Browsers tend to indent the contents of the
<q>:
The <q> element is used for shorter quotes
<q>This element is used for shorter quotes </p>
The Result:
This element is used for
shorter quotes </p>
Abbreviations & Acronyms:<abbr>
<abbr title=”Professor”>Prof</abbr>
The Result:
Prof
Citations:<cite>
When you are referencing a piece of work such as a book, film or research paper, the text will be italic
<cite>a work name</cite> by auther
The Result: a work name by auther
Definitions:<dfn>
The <dfn> element is used to indicate the defining instance of a new term.the text will be italic
A <dfn>black hole</dfn>
The Result: A black hole
Author Details:<address>
<address> <a href=”mailto:homer@example.org”> \homer@example.org</a>
<p>742 Evergreen Terrace, Springfield.</p> </address>
The Result:
homer@example.org742 Evergreen Terrace, Springfield.
Changes to Content: <ins><del><s>
It was the <del>worst</del> <ins>best</ins> idea <s>Was $995</s>
The Result:
It was the worst best idea Was $995
Summary
Text
- HTML elements are used to describe the structure of the page (e.g. headings, subheadings, paragraphs).
- They also provide semantic information (e.g. where emphasis should be placed, the definition of any acronyms used, when given text is a quotation)
Chapter : “Introducing CSS”
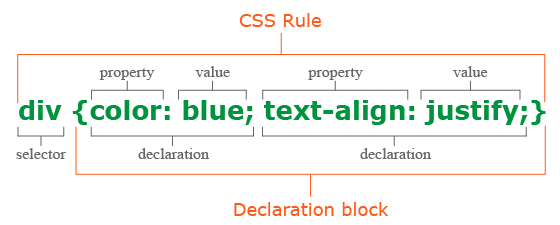
CSS allows you to create rules that control the way that each individual element (and the contents of that element) is presented.
selector:
indicate which element the rule applies to.
declaration:
indicate how the elements referred to in the selector should be styled.
- parts od declaration:
- property: indicate the aspects of the element you want to change
- value: specify the settings you want to use for the chosen properties
Summary
INTRODUCING CSS
- CSS treats each HTML element as if it appears inside its own box and uses rules to indicate how that element should look.
- Rules are made up of selectors (that specify the elements the rule applies to) and declarations (that indicate what these elements should look like).
- Different types of selectors allow you to target your rules at different elements.
- Declarations are made up of two parts: the properties of the element that you want to change, and the values of those properties. For example, the font-family property sets the choice of font, and the value arial specifies Arial as the preferred typeface.
- CSS rules usually appear in a separate document, although they may appear within an HTML page.