reading-notes
This Repo required for Asac labs class 2
Project maintained by ManarAbdelkarim Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Chapter 4: “Links”
what is a link in HTML ?
Links are the defining feature of the web because they allow you to move from one web page to another — enabling the very idea of browsing or surfing
How to write Links>
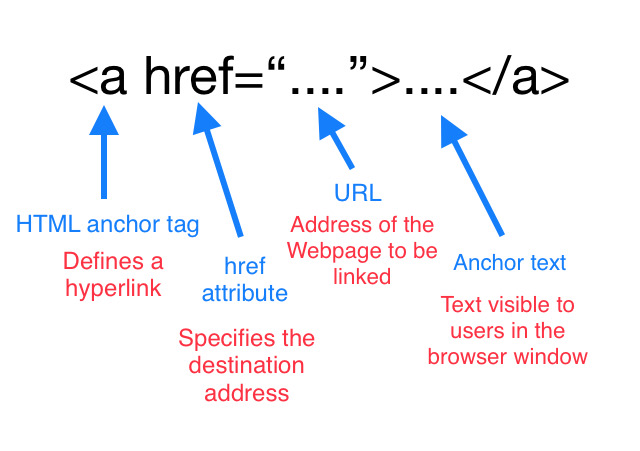
Links are created using the <a> element. Users can click on anything between the opening <a> tag and the closing </a> tag. You specify which page you want to link to using the href attribute. Writing Links
What is <a> tag?
The <a> tag defines a hyperlink, which is used to link from one page to another.<a>indicate the link’s destination. If the href attribute is present, pressing the enter key while focused on the <a> element will activate it.
Linking to Other Pages on the Same Site
-
absolute URL: When you link to a different website, the value of the href attribute will be the full web address for the site, which is known as an
-
relative URL: When you are linking to other pages within the same site, you do not need to specify the domain name in the URL.
Directory Structure
- Structure:
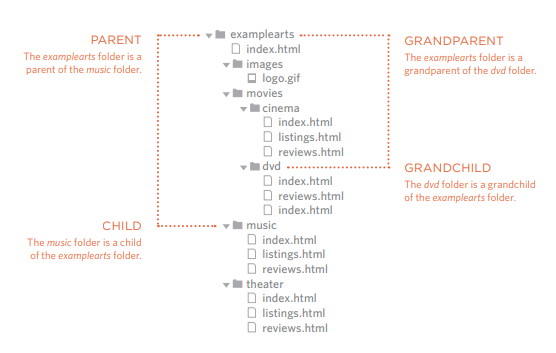
The directory structure is the organization of files into a hierarchy of folders.Computers have used the folder metaphor for decades as a way to help users keep track of where something can be found.
- Relationships
The relationship between files and folders on a website is described using the same terminology as a family tree.The top-level folder is known as the root folder.
- Homepages
The main homepage of a site written in HTML (and the homepages of each section in a child folder) is called index.html.
Relative URLs
what do we mean by Relative URLs?
Relative URLs can be used when linking to pages within your own website. They provide a shorthand way of telling the browser where to find your files.
Relative Link Type
- Same Folder:
- ex (parentDir.png)
- Child Folder
- ex (img/parentDir.png)
- Grandchild Folder
- ex (reading-notes/img/parentDir.png)
- Parent Folder
- ex (../parentDir.png)
- GrandParent Folder
- ex (../../parentDir.png)
Email Links
How to write an Email link ?
<a> tag provides you option to specify an email address to send an email. While using <a> tag as an email tag, you will use mailto: email address along with href attribute.
What is mailto?
Mailto link is a type of HTML link that activates the default mail client on the computer for sending an e-mail.
Example:
<a href = "mailto: abc@example.com">
Send Email</a>
Result:
Opening Links in a New Window
What is a target?
The target attribute specifies a name or a keyword that indicates where to display the response that is received after submitting the form.
Linking to a Specific Part of the Same Page
to link to a specific part in the same page you should use the id attribute og that part
ex <a id=”anchor-name”>Section name</h2>
How to Link to a Specific Part of Another Page?
As long as the page you are linking to has id attributes that identify specific parts of the page
ex <a href=”http:abc@example.com/ #anchor-name”>
Summary
LINKS
- Links are created using the <a> element.
- The <a> element uses the href attribute to indicate the page you are linking to.
- If you are linking to a page within your own site, it is best to use relative links rather than qualified URLs.
- You can create links to open email programs with an email address in the “to” field.
- You can use the id attribute to target elements within a page that can be linked to.
Chapter 15: “Layout”
Controlling the Position of Elements
Normal Flow
What is Normal Flow?
Normal flow is how the browser lays out HTML pages by default when you do nothing to control page layout. Elements on webpages lay themselves out according to normal flow - until we do something to change that.
Flexbox Layout
What is Flexbox?
Flexbox is a one-dimensional layout method for laying out items in rows or columns. Items flex to fill additional space and shrink to fit into smaller spaces. This article explains all the fundamentals.
Grids Layout
What is Flexbox?
Flexbox is the short name for the Flexible Box Layout Module, it is a two-dimensional layout system for the web. #### how to use Flexbox?
To use flexbox, you apply display: flex to the parent element of the elements you want to lay out
Example:
<div style="display: flex;">
<div>One</div>
<div>Two</div>
<div>Three</div>
</div>
The Result:
Floating Elements
#### What is Float ?
Floating an element changes the behavior of that element and the block level elements that follow it in normal flow. The element is moved to the left or right and removed from normal flow, and the surrounding content floats around the floated item.
Note:
The floated element becomes a block-level element around which other content can flow.
The float property values:
- left
- right
- none
- inherit
Example:
<div style="background-color:yellow; height:40px;">
<p style="background-color:red;float:left" >Float Left</p>
<p style="background-color:red;float:right" >Float right</p>
<p style="background-color:red;float:inherit;" > Float inherit</p>
</div>
The Result:
Float Left
Float right
Float inherit
Clearing Floats
- clear: left;
- clear: right;
- clear: both;
Positioning
What does Positioning do?
Positioning allows you to move an element from where it would be placed when in normal flow to another location. Positioning isn’t a method for creating your main page layouts
types of positioning:
-
Static positioning is the default that every element gets
-
Relative positioning allows you to modify an element’s position on the page,
<div> <p style="position: relative; background: rgba(255,84,104,.3); border: 2px solid rgb(255,84,104); top: 30px; left: 30px;">hi</p> <p>here another paragraph to see how it work <p> </div>
hi
here another paragraph to see how it work
-
Absolute positioning moves an element completely out of the page’s normal layout flow
<div style="width = 50% ;height: 40px;"> <p style="position: absolute; background: rgba(255,84,104,.3); border: 2px solid rgb(255,84,104); top: 30px; left: 30px;">hi there </p> <p>here another paragraph to see how it work </p> </div> -
Fixed positioning is very similar to absolute positioning, except that it fixes an element relative to the browser viewport, not another element.
<div > <p style=" background: rgba(255,84,104,.3); border: 2px solid rgb(255,84,104); top: 70px; left: 10px;position: fixed; ">hi there </p> <p>that sticky "hi there" is the result XD </p> </div>
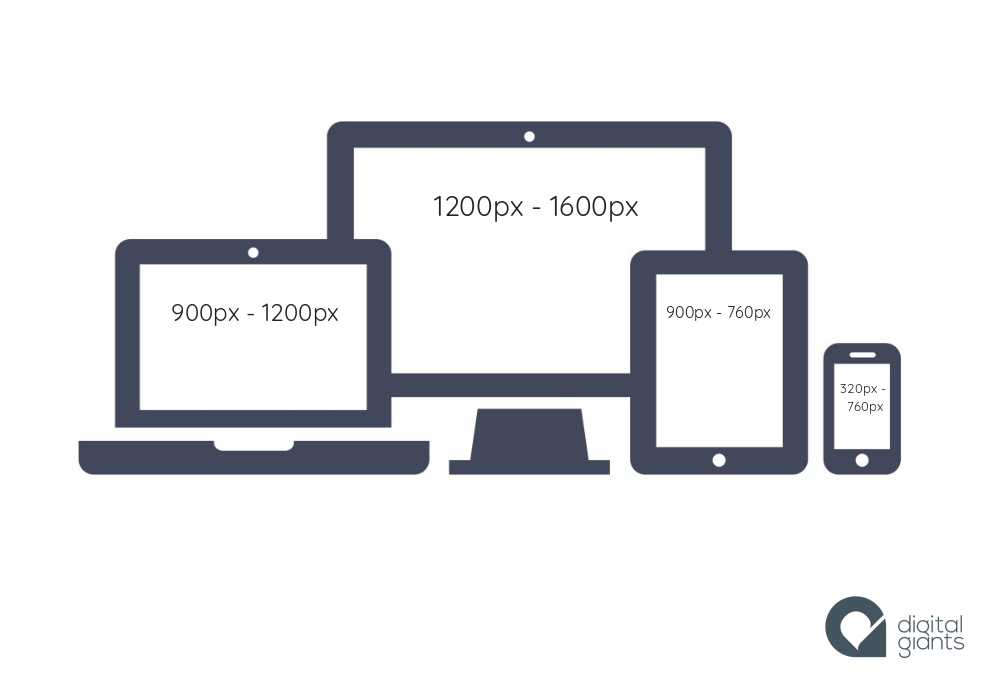
Screen Sizes
Different visitors to your site will have different sized screens that show different amounts of information, so your design needs to be able to work on a range of different sized screens.
Screen Resolution
Resolution refers to the number of dots a screen shows per inch. Some devices have a higher resolution than desktop computers and most operating systems allow users to adjust the resolution of their screens.
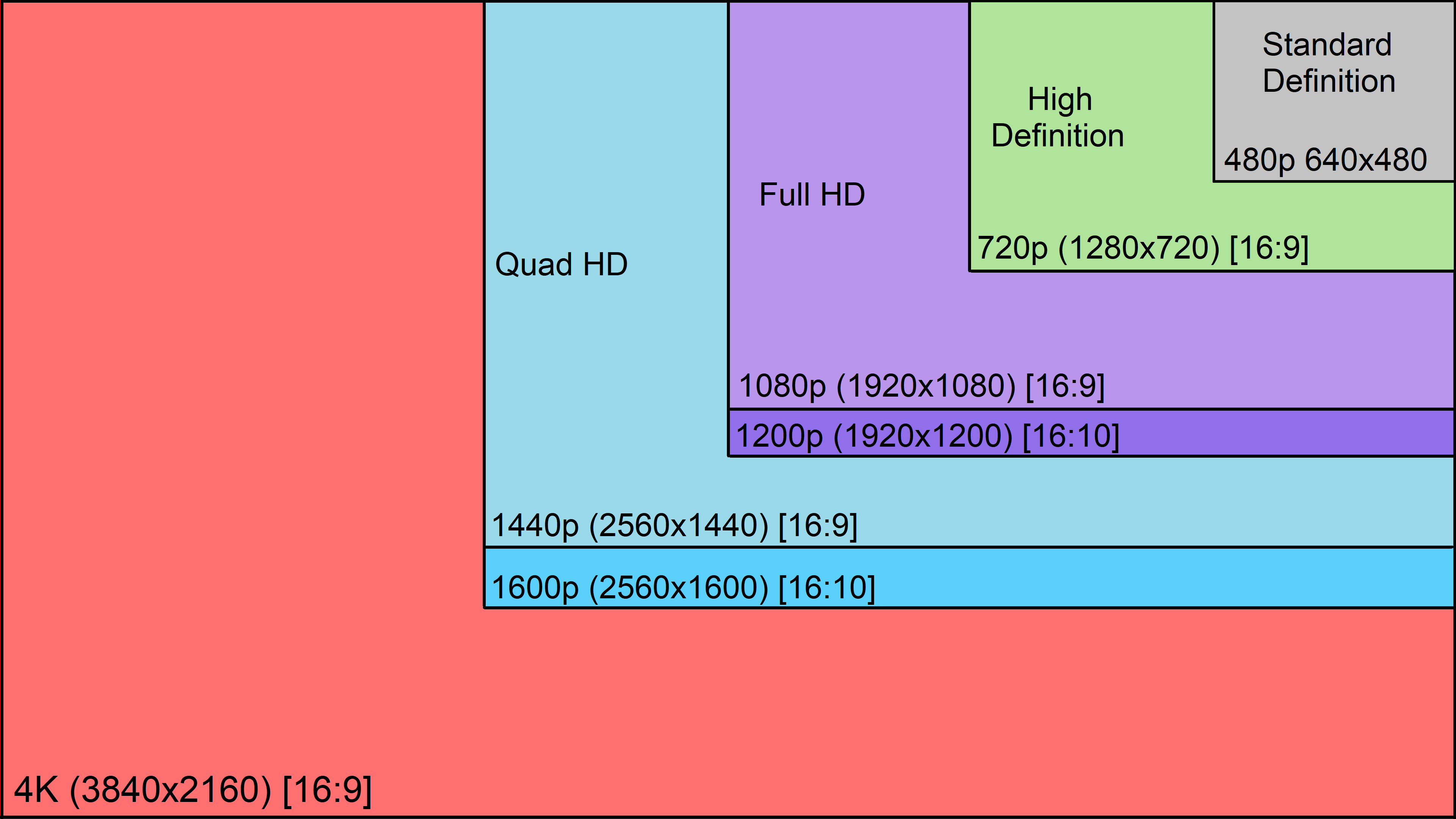
Page Sizes
Before smartphones and tablets became popular, web designers created fixed width pages that worked on the most common screen sizes - but now because screen sizes and display resolutions vary so much
Chapter 3: “Functions, Methods, and Objects”
WHAT IS A FUNCTION?
Functions let you group a series of statements together to perform a specific task. If different parts of a script repeat the same task, you can reuse the function (rather than rep eating the same set of statements). Functions consist of a series of statements that have been grouped together because they perform a specific task.
What is a method?
Method is the same as a function, except methods are created inside (and are part of) an object.
What is an Objects?
Objects are made up of properties and methods.

Function Name(Identifier):
In order to call the function later in your code, you must give it a name, so these are known as named functions.

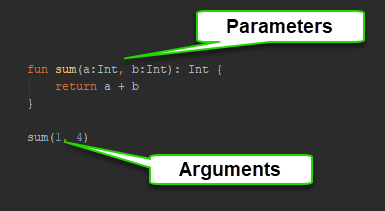
Parameter and Argument
What is the parameters?
Parameters are variables listed as a part of the function definition when the function needs to be provided with information in order to achieve a given task.
What is the Arguments?
Arguments are values passed to the function when it is invoked.
Declaring a Function:
To give the function a name and then write the statement needed to achieve its task inside the curly braces.
Calling a Function:
Execute all of the statements between its curly braces with just one line of code. calling
Declaring Functions that need information: parameters
ANONYMOUS FUNCTIONS & FUNCTION EXPRESSIONS:
Expressions produce a value. They can be used where values are expected. If a function is placed where a browser expects to see an expression, (e.g., as an argument to a function), then it gets treated as an expression.
IMMEDIATELY INVOKED FUNCTION EXPRESSIONS (IIFE):
Pronounced “iffy,” these functions are not given a name. Instead, they are executed once as the interpreter comes across them.
VARIABLE SCOPE:
Scope determines the accessibility (visibility) of these variables.The location where you declare a variable will affect where it can be used within your code. If you declare it within a function, it can only be used within that function.
types of scope:
-
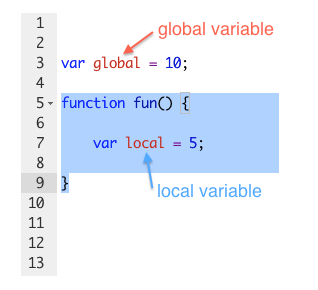
LOCAL VARIABLES : When a variable is created inside a function using the var keyword, it can only be used in that function. It is called a local variable or function-level variable.
-
GLOBAL VARIABLES:
any variable that declared outside all functions or curly braces ({}) If you create a variable outside of a function, then it can be used anywhere within the script. It is called a global variable and has global scope.
HOW MEMORY & VARIABLES WORK:
Variables that are usable only in a specific part of your code are considered to be in a local scope. Global variables use more memory.
Should I diclare locally or globally?
The browser has to remember them for as long as the web page using them is loaded. Local variables are only remembered during the period of time that a function is being executed. So that , if we need the variable temprorily for one function it is better to use local scope