reading-notes
This Repo required for Asac labs class 2
Project maintained by ManarAbdelkarim Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Debugging
- to learn how to solve programming errors we should know about :
- THE CONSOLE & DEV TOOLS
- Tools built into the browser
that help you hunt for errors.
- COMMON PROBLEMS
- Common sources of errors,
and how to solve them.
- HANDLING ERRORS
- How code can deal with potential errors gracefully.
ORDER OF EXECUTION :
To find the source of an error, it helps to know how scripts are processed.
The order in which statements are executed can be complex; some tasks
cannot complete until another statement or function has been run.
EXECUTION CONTEXTS
The JavaScript interpreter uses the concept of execution contexts. There is one global execution context; plus, each function creates a new new execution context. They correspond to variable scope.
THE STACK
The JavaScript interpreter processes one line of code at a time. When a statement needs data from another function, it stacks (or piles) the new function on top of the current task.
### EXECUTION CONTEXT & HOISTING Each time a script enters a new execution context, there are two phases of activity:
- PREPARE
-
The new scope is created
-
Variables, functions, and arguments are created
-
The value of the this keyword is determined
- EXECUTE
- Now it can assign values to variables
- Reference functions and run their code
- Execute statements
hoisting
The preparation phase is often described as taking all of the variables and functions and hoisting them to the top of the execution context.
UNDERSTANDING SCOPE
### lexical scope: Functions in JavaScript are said to have lexical scope. They are linked to the object they were defined within. So, for each execution context, the scope is the current execution context’s variables object, plus the variables object for each parent execution context.
UNDERSTANDING ERRORS
exception:
If a JavaScript statement generates an error, then it throws an exception. At that point, the interpreter stops and looks for exception-handl ing code.
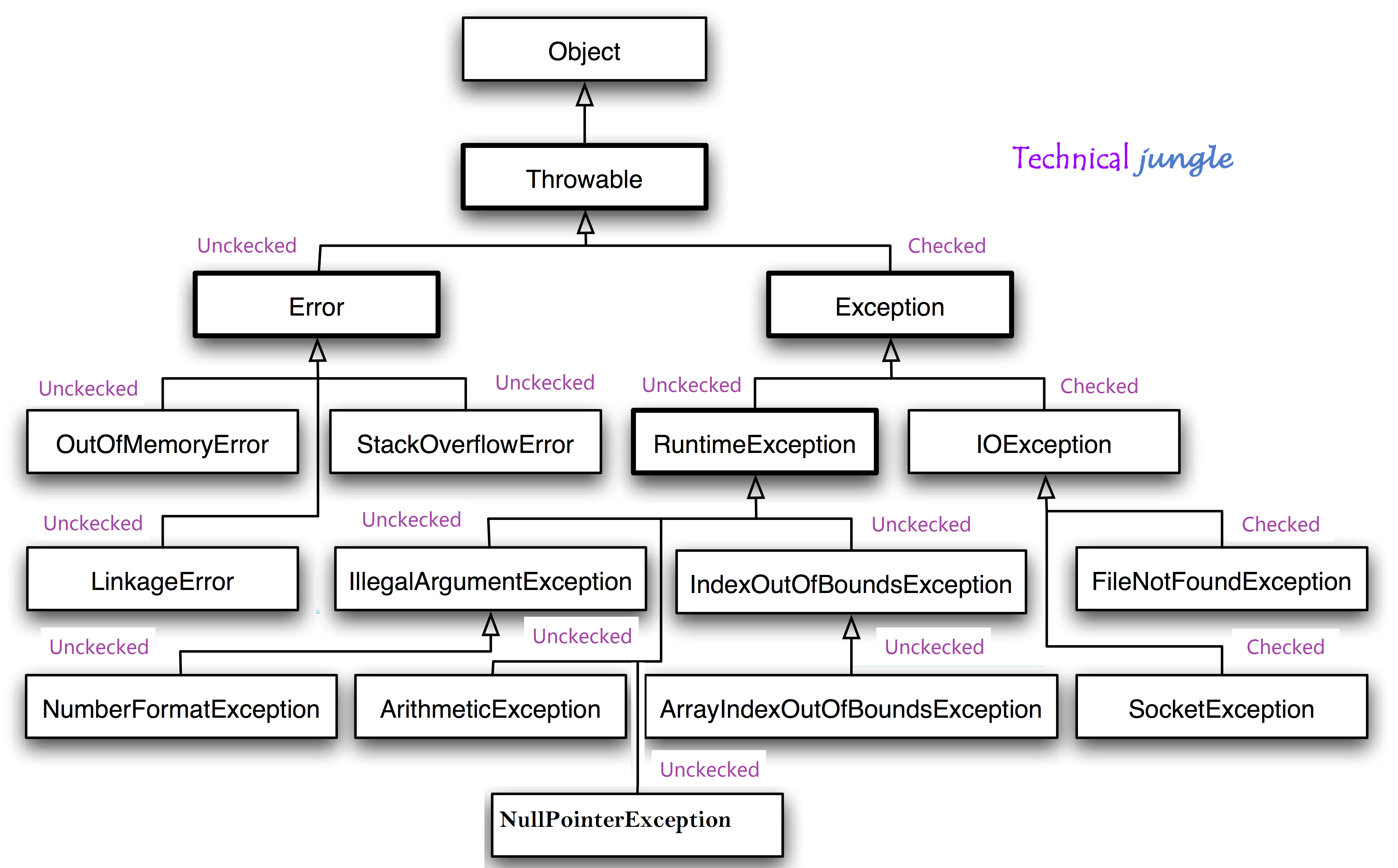
ERROR OBJECTS:
Error objects can help you find where your mistakes are and browsers have tools to help you read them.
When an Er ror object is created, it will contain the following properties:
- PROPERTY DESCRIPTION
- name Type of execution
- message Description
- file eNumber Name of the JavaScript file
- line neNumber Line number of error

Error object types:
- Eval Error
INCORRECT USE OF eval() FUNCTION The eval () function evaluates text through the interpreter and runs it as code.
- URI Error
INCORRECT USE OF URI FUNCTIONS If these characters are not escaped in URls, they will cause an error: / ? & I : ;
- Type Error
VALUE IS UNEXPECTED DATA TYPE This is often caused by trying to use an object or method that does not exist.
- RangeError NUMBER OUTSIDE OF RANGE If you call a function using numbers outside of its accepted range.
Note:
NaN NOT AN ERROR! If you perform a mathematical operation using a value that is not a number, you end up with the value of NaN, not a type error. NOT A NUMBER
HOW TO DEAL WITH ERRORS
-
DEBUG THE SCRIPT TO FIX ERRORS:
- you will need to debug the code, track down the source of the error, and fix it.
-
HANDLE ERRORS GRACEFULLY:
- You can handle errors gracefully using try, catch, throw, and f i na 1 ly statements.
A DEBUGGING WORKFLOW :
Debugging is about deduction: eliminating potential causes of an error.
BREAKPOINTS:
You can pause the execution of a script on any line using breakpoints. Then you can check the values stored in variables at that point in time.
CONDITIONAL BREAKPOINTS
You can indicate that a breakpoint should be triggered only if a condition that you specify is met. The condition can use existing variables.
DEBUGGER KEYWORD:
You can create a breakpoint
in your code using just the
debugger keyword

HANDLING EXCEPTIONS
-
TRY
- First, you specify the code that you think might throw an exception within the try block.
-
CATCH
- If the try code block throws an exception, catch steps in with an alternative set of code.
-
FINALLY
- The contents of the fina11y code block will run either way - whether the try block succeeded or failed.
THROWING ERRORS
you can generate your own errors before the interpreter creates them.
SUMMARY
-
ERROR HANDLING & DEBUGGING If you understand execution contexts (which have two stages) and stacks, you are more likely to find the error in your code.
-
Debugging is the process of finding errors. It involves a process of deduction.
-
The console helps narrow down the area in which the error is located, so you can try to find the exact error.
-
JavaScript has 7 different types of errors. Each creates its own error object, which can tell you its line number and gives a description of the error.
-
If you know that you may get an error you can handle it gracefully using the try, catch, finally statements. Use them to give your users helpful feedback.
